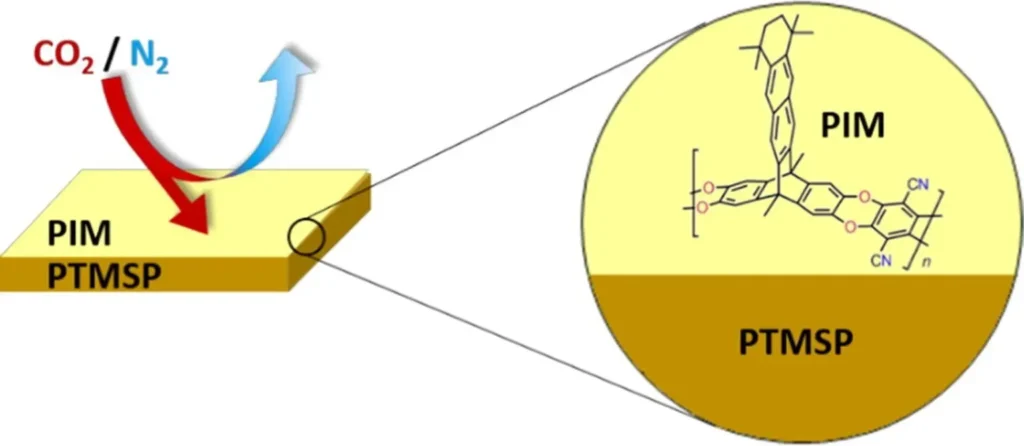
Thin film deposition research
Alicat has been cited in over 1,000 peer-reviewed research papers. The following papers focus on thin film deposition and emerging technologies in that field. Contact us if you’d like your research to be highlighted.
An influence of oxygen flow rate on structural, optical and tribological properties of molybdenum oxide thin films
Abstract
The influence of oxygen flow rate is examined on structural, optical and tribological properties of molybdenum oxide films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. The films were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope (SEM), and contact angle measurement system. The optical properties of the films were measured by UV-Vis-NIR spectrophotometer and transmittance of ∼73% in the visible region of the spectrum was achieved. The band gap increases with increases in oxygen gas flow rate. AFM figure illustrates that the roughness of surface increases as oxygen flow rate increases. As oxygen increases wear rate and COF decreases while at the 18 sccm the lowest wear rate found.
Reference
Dave, D. P., Patel, A. M., Chauhan, K. V., & Rawal, S. K. (2021). An influence of oxygen flow rate on structural, optical and tribological properties of molybdenum oxide thin films. Advanced Engineering Forum, 39, 43–53. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/aef.39.43
Highly sensitive room temperature hydrogen sensor based on undoped SnO2 thin films
Abstract
The physicochemical property of semiconductors play a vital role in enhancing the gas sensing performance of the metal oxides that can operate in real time atmosphere. Here in, hydrogen (H2) sensing behaviour of SnO2 thin films prepared using DC reactive magnetron sputtering technique by varying the cathode power are reported. From X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, polycrystalline nature of SnO2 thin films were observed and it exhibited rutile tetragonal structure and the crystallite size was found to be increased from 17.6 to 38.8 nm. From the morphological study taken from field emission-scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), the nano granular like morphology was observed. As a result of increase in cathode power, the optical bandgap reduced from 3.5 to 3.3 eV. The influence of cathode power on the sensitivity, response and recovery time have been studied. This report elucidates the H2 sensing response towards undoped SnO2 thin films of about 4.7 at room temperature towards 100 ppm concentration.
Reference
Abinaya, M., Pal, R., & Sridharan, M. (2019). Highly sensitive room temperature hydrogen sensor based on undoped SnO2 thin films. Solid State Sciences, 95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2019.105928
The impact of O2/Ar ratio on morphology and functional properties in reactive sputtering of metal oxide thin films
Abstract
Morphology is a critical parameter for various thin film applications, influencing properties like wetting, catalytic performance and sensing efficiency. In this work, we report on the impact of oxygen partial flow on the morphology of ceramic thin films deposited by pulsed DC reactive magnetron sputtering. The influence of O2/Ar ratio was studied on three different model systems, namely Al2O3, CuO and TiO2. The availability of oxygen during reactive sputtering is a key parameter for a versatile tailoring of thin film morphology over a broad range of nanostructures.
TiO2 thin films with high photocatalytic performance (up to 95% conversion in 7 h) were prepared, exhibiting a network of nanoscopic cracks between columnar anatase structures. In contrast, amorphous thin films without such crack networks and with high resiliency to crystallization even up to 950 °C were obtained for Al2O3. Finally, we report on CuO thin films with well aligned crystalline nanocolumns and outstanding gas sensing performance for volatile organic compounds as well as hydrogen gas, showing gas responses up to 35% and fast response in the range of a few seconds.
Reference
Vahl, A., Dittmann, J., Jetter, J., Veziroglu, S., Shree, S., Ababii, N., Lupan, O., Aktas, O. C., Strunskus, T., Quandt, E., Adelung, R., Sharma, S. K., & Faupel, F. (2019). The impact of O2/ar ratio on morphology and functional properties in reactive sputtering of metal oxide thin films. Nanotechnology, 30(23), 235603. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab0837
The fabrication of ultrathin films and their gas separation performance from polymers of intrinsic microporosity with two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) chain conformations
Abstract
The expansion of the use of polymeric membranes in gas separation requires the development of membranes based on new polymers with improved properties and their assessment under real operating conditions. In particular, the fabrication of ultrathin films of high performance polymers that can be used as the selective layer in composite membranes will allow large reductions in the amount of the expensive polymer used and, hence, the cost of membrane fabrication.
In this contribution, two polymers of intrinsic microporosity (PIMs) with very different chain configurations (two-dimensional, 2D, chains or conventional contorted three-dimensional, 3D, conformation) have been compared in their ability to form ultrathin films, showing the relevance of polymer design to obtain compact and defect-free films.
Monolayers of the 2D polymer PIM-TMN-Trip can be efficiently deposited onto poly[1-(trimethylsilyl)-1-propyne] (PTMSP) to obtain composite membranes with a CO2/N2 selectivity similar to that of the corresponding thick membranes of the same PIM using only a small fraction of the selective polymer (less than 0.1%).
Reference
Benito, J., Vidal, J., Sánchez-Laínez, J., Zornoza, B., Téllez, C., Martín, S., Msayib, K. J., Comesaña-Gándara, B., McKeown, N. B., Coronas, J., & Gascón, I. (2018). The fabrication of Ultrathin Films and their gas separation performance from polymers of intrinsic microporosity with two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) chain conformations. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 536, 474–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.10.075
Examination of various characteristics for sputtered tantalum oxide-nitride thin films deposited at various oxygen flowrates
Abstract
Tantalum oxynitride thin films were prepared by reactive sputtering. The argon and nitrogen flow rate were kept stable whereas oxygen flow rate was incremented periodically. The effect of oxygen flow rate on various properties of tantalum oxynitride thin films is reported in this research paper. XRD patterns of tantalum oxynitride thin films displayed peaks commonly as for nano-crystalline materials. Surface topography observed to be smooth and exhibited smaller grain structure. Wettability test showed promising results for hydrophobicity. Wear test was done on uncoated and coated tantalum oxynitride thin films on 10 mm diameter cylindrical pins of brass and mild steel.
Reference
Gandhi, A. A., Chauhan, K. V., Kapopara, J. M., Jariwala, N. N., & Rawal, S. K. (2017). Examination of various characteristics for sputtered tantalum oxide-nitride thin films deposited at various oxygen flowrates. Integrated Ferroelectrics, 185(1), 41–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2017.1370286